Electric motors reduce noise pollution in assembly applications
Introduction
Noise is a common occupational hazard in a large number of workplaces because industrial machinery and processes consist of many and varied noise sources. Both the WHO and EU consider long-term noise levels above 55 dB(A) to be potentially damaging to health. OSHA recommends that workers should not be exposed to a noise level of more than 85 dB(A), averaged over an eight-hour working day.
Noise from pneumatic machinery
For this article, we will focus only on air compressors and pneumatic motors. Air compressors are generally extremely noisy. The noise is caused by trapping a definite volume of air and carrying it around the case to the outlet at higher pressure. The pressure pulses from compressors are quite severe and noise levels can exceed 105 dB(A).
The noise from an air motor consists of both mechanical noise and a pulsating noise from air flowing out of the outlet. The outlet air creates a noise level that can reach 115 dB(A) if the air is allowed to exhaust freely into the atmosphere. An exhaust silencer can be fitted to reduce this noise, but it will generate back-pressure on the outlet side of the motor if it is too small or blocked, which will reduce the motor’s power.
Compressed air-powered equipment is widely used within different industries. This equipment generates noise through contact between the machine and the working surface;, through exhaust air noise caused by the turbulent flow generated as the compressed air passes the motor and by the aerodynamic noise generated in the air exhaust;, and from sound radiation from tool vibration caused by airflow inside the equipment. The noise level can reach as high as 110 dB(A) at the operator’s ear.
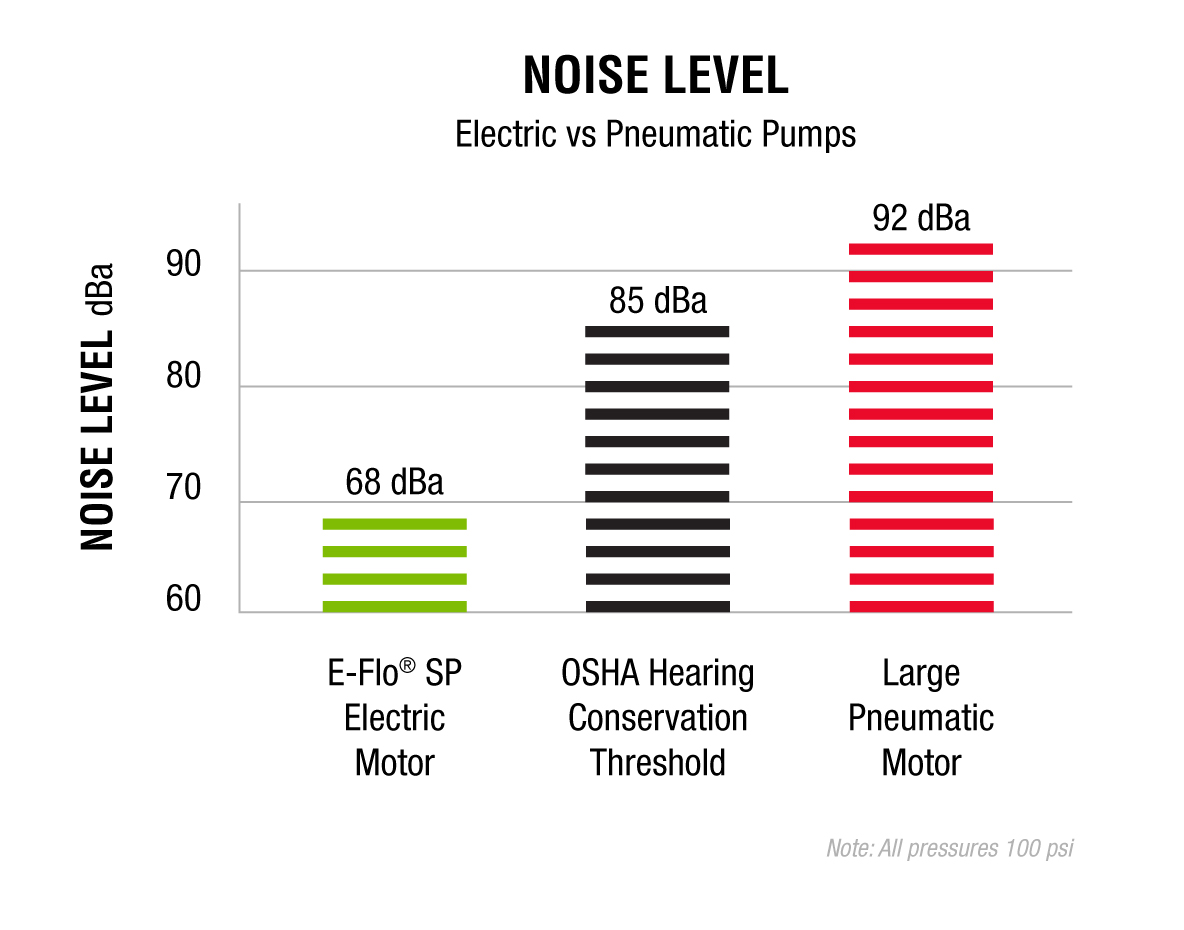
Reducing noise levels by using electric motors and pumps
The easiest way to reduce noise pollution is to eliminate the source of hazardous noise. When elimination is not possible, the substitution of loud equipment for quieter equipment may be the next best alternative to protect workers from hazardous noise.
Electric motors have a number of advantages compared to pneumatic motors. One advantage at the top of the list of benefits is quieter operation. Graco’s noise reduction technology in its electric motors helps lower noise levels throughout an industrial facility. In turn, operators experience more comfortable working conditions.
For example, the Graco E-Flo SP (dual control) electric circulating pump operates at a noise level of only 68 dB(A) compared to the 92 dB(A) of a comparable pneumatic pump. It is a whole 17 dB(A) lower than OSHA’s sound regulation for the industrial workplace of 85 dB(A). This creates a much quieter, more comfortable, and healthier workplace and allows operators to remain near the equipment to ensure continuous performance.
Other examples include Graco’s electric sealant and adhesive equipment line, which can be tailored for one or two-component applications. Three popular products are:
- The E-Flo SP electric pumps and supply pumps are designed for industrial and automotive sealant and adhesive applications. This advanced pump will drastically increase efficiency, improve system control capabilities, optimise process performance, and provide critical performance data. At normal operation, its sound level is 70 dB(A).
- The new E-Flo iQ one component metering and dispense system greatly simplifies robotic application of sealants and adhesives. Since the E-Flo iQ uses an electric servo-driven motor, the sound level is often less than 70 dB(A).
- The Electric Fixed Ratio (EFR) meter, mix and dispense system is an extremely quiet (70 dB(A)), electrically-driven, proportioner for two-component sealant and adhesives. The EFR provides advanced material control in applications requiring consistent shots and beads.
Contact an expert
Related Articles
Four maintenance advantages of using electric motors for assembly applications
To power a pump, do you choose an electric or a pneumatic motor? Here are the key maintenance considerations for choosing an electric motor.
Four reasons why electric motors are the greener solution
Industrial manufacturing companies are moving from air to electric to reduce their costs and environmental footprint.
Why electric motors improve the quality and precision of the dispense for 1k metering
Electric motors have the capability to drive the pump lower more intelligently and therefore dispense an accurate bead without the need for an intermediate metering device.





