How to master fluid and material properties of a diaphragm pump
To get the best performance out of your pump, you need to select the right pump with the right components for every application.
Graco’s Husky Air-Operated Double Diaphragm (AODD) pumps are one of the most reliable and efficient pumps on the market. But to get the best performance out of them means selecting the right pump with the right components for every application.
The Graco Husky AODD pump comes in a wide range of metal and plastic configurations, including ATEX models. The seat, balls and diaphragm are made from a variety of different materials. Each material offers specific advantages.
Before choosing a pump, it’s good to know what materials are best for which applications, including corrosive and abrasive fluid transfer.
Method of operation
An Air-Operated Double Diaphragm (AODD) pump is a type of positive displacement pump that uses compressed air as a power source. The compressed air is shifted from one chamber to the other by a linked shaft that allows the chambers to move simultaneously. This back-and-forth motion forces liquid out of one chamber and into the outlet manifold, while filling the opposite fluid chamber via the inlet manifold. Upon changeover, the fluid section that was filled on the previous shift empties into the outlet manifold and fills the opposite chamber via the inlet manifold. The rapid changeover allows for reduced pulsation at the outlet.
What are you pumping?
Before choosing your pump, it’s helpful to understand what kind of fluid or substance you want it to pump. There are a number of questions to consider.
- What is the make-up of the fluid in terms of solid content?
- What is its pH? What is its viscosity (cps), density and specific gravity?
- Is the fluid abrasive?
The answers to these questions will have an impact on the material you choose for the pump’s seat, balls and diaphragm. Your first action is to take a good look at the fluid’s technical data sheet. Don’t forget that many substances are thixotropic, which means their viscosity decreases when a stress is applied, for example by stirring. Mayonnaise, tomato ketchup, glue and zinc epoxy are good examples, and certain paints are also thixotropic.
A generalization is that the ball of the pump needs to be at least 10% heavier than the fluid you are trying to pump to ensure a good seal between the ball and the seat. In other words, the denser and more viscous a substance – such as honey and ketchup – the heavier the ball needs to be and the softer the seat. Because with a high density substance you need the ball to close quickly onto the seat for optimal efficiency. On the other hand, if you are pumping a light oil with a low viscosity, using a heavy ball is not necessary – and the pump will make a lot of unnecessary noise.
The chemical action of some substances is also a critical factor. Vinegar, for example, makes aluminum oxidize, and will affect some plastics. A number of chemicals are also highly corrosive.
Many fluids are abrasive. For example, zinc epoxy contains zinc flakes, while certain topcoat paints contain abrasive aluminum or other metallic flakes. Such substances can destroy some materials, or at least scratch them. Fillers can contain hard mica or can be soft like talc. For a hard filler, a soft or stainless ball is better, as these can’t be scratched, while the diaphragm also has to be as soft as possible.

Which pump body to choose?
The Husky pump is available with a plastic or metal body. Graco’s plastic pumps are constructed from either acetal, polypropylene or Kynar® (polyvinylidene fluoride, PVDF).
Acetal provides good resistance to solvents and coatings but not against acids or bases. It is groundable and offers protection in ATEX environments. This makes an acetal pump ideal for solvents and paints.
Polypropylene is low in price and is resistant to most acids and bases. However, in its virgin state it can not be grounded. When pumping flammable liquids or chemicals, it is best to use a groundable pump. Some Husky pumps are made with polypropylene that contains a conductive additive, which makes the wetted parts conductive. These pumps can then be grounded and can be used to pump flammable liquids.
Kynar® is ideal for extremely aggressive environments such as acids and bases, but it comes with a high price ticket.
The bodies of Graco’s metal pumps are made from aluminum, ductile iron, or stainless steel. Aluminum is a good material for neutral substances. It’s rugged, easily groundable, and is the lowest priced metal pump. Ductile iron is the best choice for light caustic substances of pH 4-5 or 9-10. It’s rugged and groundable, and is excellent for water treatment and filter press applications. Stainless steel is a good match for sanitary applications. It offers wide chemical compatibility and good abrasion resistance, and is of course groundable. Of the three metal pumps, stainless steel is the most expensive, with aluminum the cheapest.
Which seats, balls and diaphragms to choose?
For seats, balls and diaphragms a vast number of materials can be selected.
Santoprene® is a very light and flexible material, so isn’t suitable for highly viscous substances, otherwise the ball will float. Chemically it’s similar to EPDM and can be used when you need a high pump cycle rate and high suction lifts, and when you need moderate to high chemical resistance.
Buna-N® or nitrile rubber is a highly flexible material that offers a long lifetime if used correctly. It’s typically used with very abrasive substances, although should be kept away from aggressive chemicals. It’s used a lot in the ceramics industry where it’s ideal for pumping abrasive ceramic slurries. In such applications – as well as for high viscosity substances – a Buna-N® seat can be combined well with stainless steel balls to obtain fast closure between the seat and the ball.
Viton® offers the highest chemical resistance of all the rubbers and protects against toxic and highly corrosive chemicals such as aromatic or chlorinated hydrocarbons and acids. However, it does come at a high price.
Geolast® is an oil-resistant thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) that is similar to Buna-N® but a little stiffer. It’s typically used with mild oils, petroleum-based fluids like mineral oils, and in the ceramics industry to pump abrasive slurries.
PTFE is excellent for aggressive chemicals as it is chemically neutral with most substances. It can be used at high temperatures, but displays poor resistance against abrasion. PTFE is particularly useful in the sanitary industry as it can be cleaned with steam or boiling water. However, it’s not suitable for low temperature applications. It’s also a very stiff material. If used as a diaphragm, it can be combined with a softer backing diaphragm of an EPDM rubber to give it extra flexibility. PTFE is a good material to use when you need high cycle rates.
Hytrel® is another thermoplastic elastomer that is known for its resilience, heat and chemical resistance, and good abrasion resistance. However, it’s not suitable for high temperature applications. Stainless steel offers the best abrasion resistance.

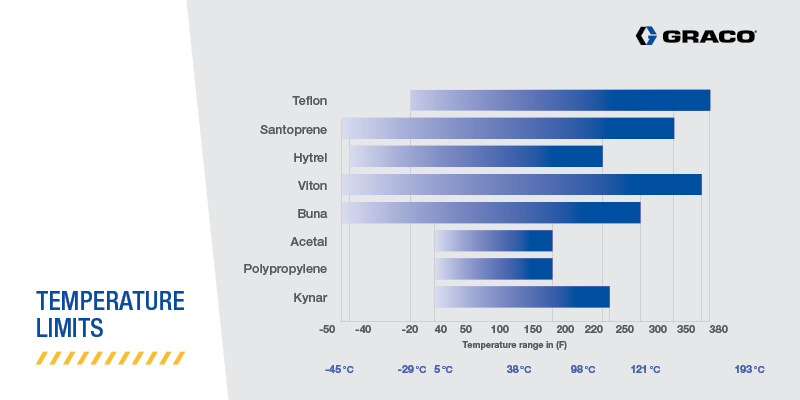
Temperature limits
It’s also important to note that each material operates optimally within a specific temperature range:
Some standard combinations
Graco tries to make the selection process easier by offering a number of standard ball-seat-diaphragm configurations for its Husky pumps:
- Hytrel®-Acetal-Hytrel®: A good combination for general purpose, water, oil and windshield cleaner pumping applications.
- Geolast®-Geolast®-Geolast®: Another general purpose configuration but with higher abrasion resistance. It’s often used in large pumps and in combination with stainless steel.
- Stainless steel-Santoprene®-Santoprene®: Offering good abrasion resistance and chemical resistance, this combination works well with a body made of aluminum, stainless steel or polypropylene.
- Acetal-PTFE-PTFE: Good for paint with a low solids content, as well as for tints and enamels. Use with a pump body made of aluminum, stainless steel or acetal.
- Stainless steel-stainless steel-PTFE: Good for high viscosity fluids, high solid content substances, and waterborne solutions. Goes well with a body made of aluminum, stainless steel or acetal.
- Polypropylene-Hytrel®-Hytrel®: Ideal for water and other neutral fluids but not solvents. Low cost, and offers a flexible diaphragm.
- Polypropylene-PTFE-PTFE: This combination offers good chemical resistance at a low cost, as well as good chemical compatibility for acids and bases.
- Stainless steel-Viton®-Viton®: A combination that works well for unleaded fuel, and for solutions used in chromium plating baths.
- Kynar®-Viton®-Viton®: A good choice for chromate solutions. Kynar® can replace Viton® in the balls if Viton® is not available.
- Kynar®-PTFE-PTFE: This is the best choice for aggressive and hot products and acids. This combination can be used with a body made from Kynar® or stainless steel.
NEED HELP TO CONFIGURE YOUR PUMP?
On its website, Graco offers a Chemical Compatibility Guide. It is an excellent general guideline for pump selection and to determine compatible materials. Another useful guide is the Materials of Construction Guide which allows you to find the most cost-effective match for your application. A third useful tool is the Pneumatic Diaphragm Pump Selector which will help you select the right pump for your specific application.
If you require further assistance, or would like to see a demonstration of a Husky AODD pump, then please fill in the contact form below.
Geolast® is a registered trademark of ExxonMobil Chemical Co. Buna-N® is a registered trademark of Pittway Corporation, Chicago. Santoprene® is a registered trademark of Advanced Elastomer Systems, L.P. Hastelloy® is a registered trademark of Haynes International, Inc. Viton® is a registered trademark of The Chemours Company. Kynar® is a registered trademark of Arkema Inc. Hytrel® is a registered trademark of DuPont.
Brain Snack: How to master fluid and material properties of a diaphragm pump? - Available on-demand
Learn more about fluid and material properties of double diaphragm pumps (AODD) during a 60 minute live webinar that covers available options of materials, when to select which material and examples of correct material choice for a certain fluid type.
Related Articles
How to select the correct Husky pump
Graco's Husky pumps are designed for a variety of industrial and chemical transfer applications. But how do you choose the best pump for a specific application? Here are a few guidelines to help.
How to configure a diaphragm pump with confidence – Part 1
The Graco website contains tools to simplify the selection and configuration of a diaphragm pump for a specific application.
How to configure a diaphragm pump with confidence – Part 2
Cristiano Giancola, Technical Training Supervisor at Graco, selects two diaphragm pumps for two different applications.



